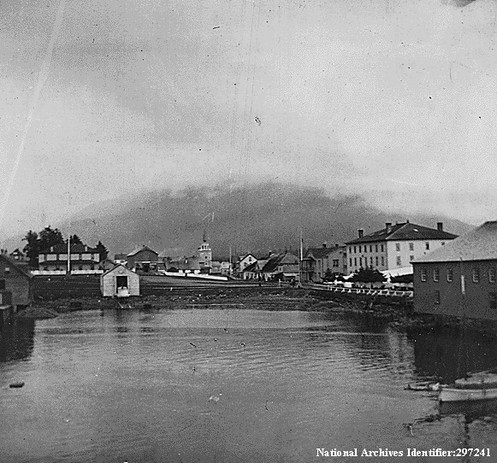Sitka (sit'-ka) (sit- kuh)
The City and Borough of Sitka are located on Baranof Island. The name is derived from a Tlingit word, “Shee At'ika,” meaning people on the outside of Shee (Baranof Island). Sitka is protected by myriad small islands and Kruzof Island where Mount Edgecumbe, a dormant volcano, is located. Baranof Island is the fourth largest island in the Alexander Archipelago, a group of about 1,100 islands located within the Tongass National Forest.
Russia was attracted to Alaska for the fur trade, mainly the sea otter pelts. The Russian-American Company was formed in 1799 and established its capital at New Archangel (Sitka). With Alexander Baranov as its first chief manager, the Russian-American Company ran Russian Alaska like the British East India Company ran India at the time. In 1802, the Tlingit, who were hostile toward the Russians, destroyed the settlement known as "Redoubt Saint Michael." Baranov returned to Sitka in 1804 with a large force of Russians and Aleuts aboard the Russian warship, Neva, and succeeded in forcing the Tlingit to retreat into the surrounding forest. Alaska was difficult to defend, and Russia did not want Britain to acquire Alaska. Also, only a few hundred Russians were living there, and the fur trade was slowing down. Therefore, in 1857, Tsar Alexander II instructed his minister in Washington to check with the American government about a sale.
Sitka is where the signing of the Alaska Purchase from Russia by the United States took place on October 18, 1867, for $7.2 million dollars. Secretary of State, William Seward, who had been appointed by Abraham Lincoln, negotiated the purchase. At the time, many regarded the deal as "Seward’s folly." But major discoveries of gold and petroleum resources, continue to prove the wisdom of that purchase!
While gold mining and fish canning helped establish Sitka after the purchase, World War II is what helped Sitka to move into its own. The small Japonski Island, which is across the Sitka Channel from Baranof Island and today is home to Sitka’s Rocky Gutierrez Airport, is connected by O'Connell Bridge to Baranof Island. The Navy constructed an air base on Japonski, with 30,000 service personnel and over 7,000 civilians. The Coast Guard maintains the air station today
The City and Borough of Sitka are located on Baranof Island. The name is derived from a Tlingit word, “Shee At'ika,” meaning people on the outside of Shee (Baranof Island). Sitka is protected by myriad small islands and Kruzof Island where Mount Edgecumbe, a dormant volcano, is located. Baranof Island is the fourth largest island in the Alexander Archipelago, a group of about 1,100 islands located within the Tongass National Forest.
Russia was attracted to Alaska for the fur trade, mainly the sea otter pelts. The Russian-American Company was formed in 1799 and established its capital at New Archangel (Sitka). With Alexander Baranov as its first chief manager, the Russian-American Company ran Russian Alaska like the British East India Company ran India at the time. In 1802, the Tlingit, who were hostile toward the Russians, destroyed the settlement known as "Redoubt Saint Michael." Baranov returned to Sitka in 1804 with a large force of Russians and Aleuts aboard the Russian warship, Neva, and succeeded in forcing the Tlingit to retreat into the surrounding forest. Alaska was difficult to defend, and Russia did not want Britain to acquire Alaska. Also, only a few hundred Russians were living there, and the fur trade was slowing down. Therefore, in 1857, Tsar Alexander II instructed his minister in Washington to check with the American government about a sale.
Sitka is where the signing of the Alaska Purchase from Russia by the United States took place on October 18, 1867, for $7.2 million dollars. Secretary of State, William Seward, who had been appointed by Abraham Lincoln, negotiated the purchase. At the time, many regarded the deal as "Seward’s folly." But major discoveries of gold and petroleum resources, continue to prove the wisdom of that purchase!
While gold mining and fish canning helped establish Sitka after the purchase, World War II is what helped Sitka to move into its own. The small Japonski Island, which is across the Sitka Channel from Baranof Island and today is home to Sitka’s Rocky Gutierrez Airport, is connected by O'Connell Bridge to Baranof Island. The Navy constructed an air base on Japonski, with 30,000 service personnel and over 7,000 civilians. The Coast Guard maintains the air station today